Final ID: P3083
Characterization of the Course of Heart Disease using Multimorbidity-adjusted Life Year (MALY): A Multi-state Non-Markov Framework
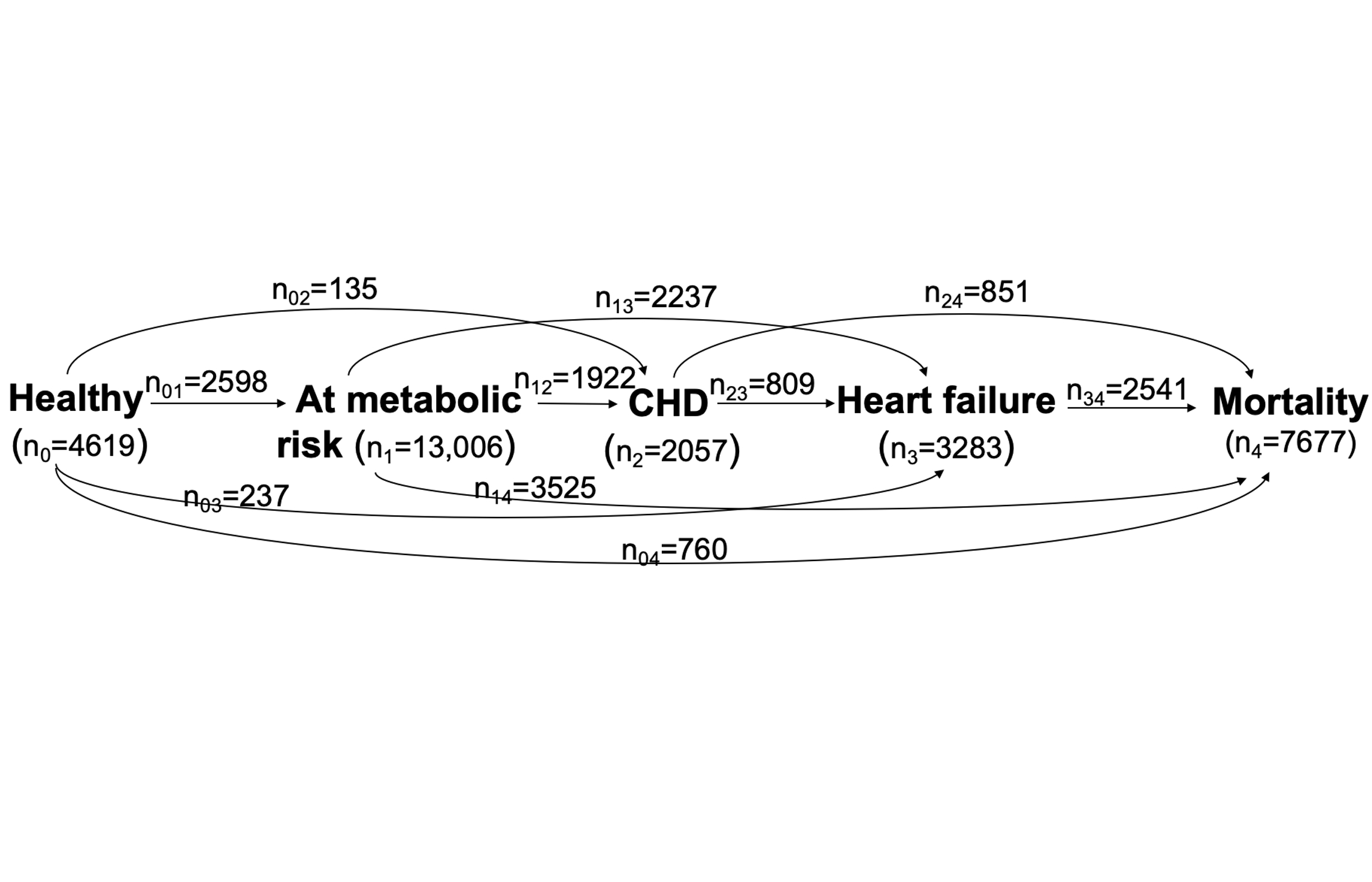
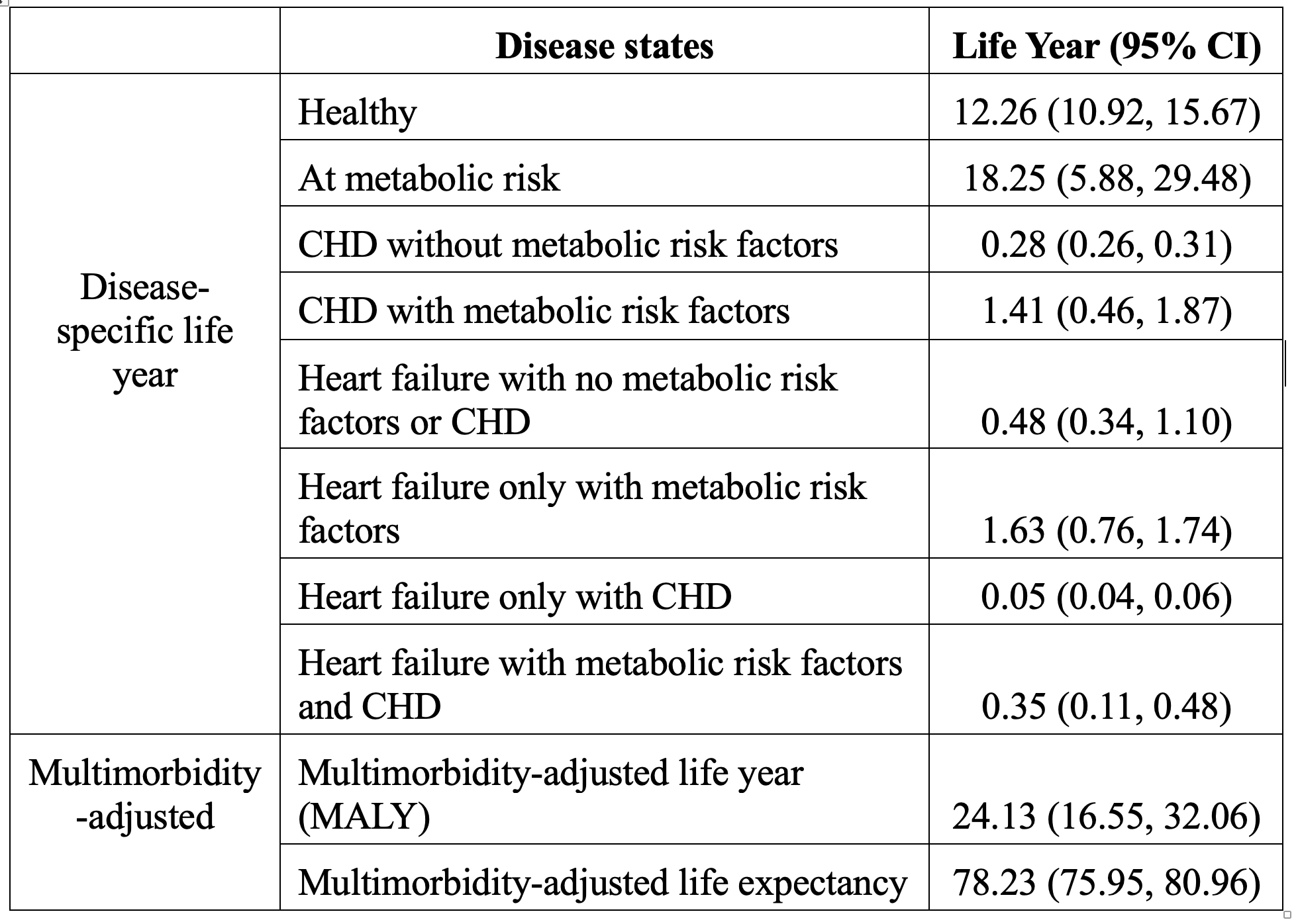
Abstract Body: Background. In cardiovascular epidemiology, heart disease has been largely investigated by focusing on a single (or composite) endpoint. A few studies examined the disease course using multi-state Markov models, assuming the current disease state is independent of past states. Markov models are unsuitable to heart disease due to three reasons: First, risk factors interplay and affect future disease risk; second, Markov assumption does not allow for multimorbidity, a common condition for heart disease; and third, the estimated transition probabilities are time-specific and indirect for public health use. Methods. We have developed a multi-state non-Markov framework that splits disease state into substates by conditioning on past states (Ding et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2024. In revision. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.18.24313882). As the substates track history of past states, transition rates between substates can be synthesized into a summary estimate, multimorbidity-adjusted life year (MALY) that represents the adjusted life year in full health. The derivation of MALY can be found in our second paper (Ding et al. medRxiv. 2024.doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.18.24313882). In this study, we applied our framework to characterize the course of heart disease among participants enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study (ARIC). ARIC data was obtained from NHLBI BioLINCC. Results. We modeled the course of heart disease in five states: healthy, at metabolic risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), heart failure, and mortality (Figure 1). The disability weights assigned to each disease state is shown in Figure 2. In this mid- to old-age population, the estimated MALY was 24.13 (95% CI: 16.55, 32.06) years (Figure 3). The multimorbidity-adjusted life expectancy was higher among women (79.29 [95% CI: 77.42, 81.57] years) than men (77.07 [95% CI: 74.37, 80.05] years), and was higher among Whites (79.04 [95% CI: 77.05, 81.31] years) than Blacks (75.49 [95% CI: 73.19, 79.30] years). Impact. MALY summarizes the course of heart disease into one estimate and can be used in comparative effectiveness of disease intervention in the near future.
More abstracts on this topic:
Burden of Stroke Attributable to Air Pollution in India and its Trend from 1990-2021: A cross State Comparative Assessment
Surana Deval, Patel Juhi, Desai Hardik, Adrejiya Parth, Singh Kushagrita, Malhans Jeevanjyot, Vala Janmay, Goel Shrey, Syed Saif, Lakkimsetti Mohit, Amin Vishrant
Apical resection preserves the proliferative capacity of cardiomyocytes located throughout the left ventricle of the heartNguyen Thanh, Nakada Yuji, Wei Yuhua, Zhang Jianyi